|
|
|
Acute myocardial infarction prevention, food diet supplements with organic lycopene
as antioxidant to protect cardiovascular activities.
Dietary food to prevent diseases as myocardial infarction, angina
pectoris, stroke, heart failure, arrythmias. |
|
|
HEART PROTECTION SUPPLEMENTS | CARDIOVASCULAR SUPPLEMENTS |
|
|
|
Cardiovascular Dietary Supplements wholesale production of heart care supplements to prevent angina pectoris, stroke, heart failure, arrythmias, acute myocardial infarction and other heart diseases with "Lycopne Diet Supplements" produced, according to the health international standards as antioxidant. |
 |
Organic health care pharmacy products: |
||
|
Italian Organic Dietary Supplements |
Made in Italy health organic food dietary supplements |
||||
|
|
EMIRATES HEART DIETARY SUPPLEMENTS MANUFACTURER FOR PHARMACY DISTRIBUTORS |
|
|
SCIENTIFIC RESEARCHES ABOUT HEART HEALTH CARE DIETARY SUPPLEMENT There are many worldwide researches defining the high power of the organic components for human heart care supplements manufacturing industry. Scientific pubblications from University in Japan, USA, Italy, Australia,... confirms the quality and efficience of the Organic Lycopene to avoid main human diseases as Parkinson, Alzheimer disease, cancer and others. The scientific staff of Pierre Italy has used all of them as scientific reference to improve, to define our organic dietary supplements... APPLY FOR DISTRIBUTION |
|
|
SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH TO CREATE LYCOMPLETE® - ITALIAN HEART CARE SUPPLEMENT MANUFACTURING |
|
|
|
CERTIFIED WORLD SCIENTIFIC RESEARCHES - ORGANIC LYCOPENE SUPPLEMENTS MANUFACTURING |
|
1 |
Rissanen T, Voutilainen S, Nyyssonen K, Salonen JT. - Research Institute of Public Health, University of Kuopio, Kuopio, Finland 70211. Lycopene, atherosclerosis, and coronary heart disease. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2002 Nov; 227(10):900-7 [File : 1ExpBiolMed2002.pdf] |
|
2 |
Rao AV. - Department of Nutritional Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada M5S 3E2. Lycopene, tomatoes, and the prevention of coronary heart disease. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2002 Nov; 227(10):908-13 [File : 2ExpBiolMed2002.pdf] |
|
3 |
Voutilainen S, Nurmi T, Mursu J, Rissanen TH.- Research Institute of Public Health and Department of Public Health and General Practice, University of Kuopio, Kuopio, Finland. Carotenoids and Cardiovascular health.Am J Clin Nutr. 2006 Jun;83(6):1265-71. [File: 3AmJClinNutr2006.pdf] |
|
4 |
Das S, Otani H, Maulik N, Das DK. Cardiovascular Research Center, University of Connecticut School of Medicine, Farmington, CT 06030-1110, USA. Lycopene, tomatoes, and coronary heart disease. Free Radic Res. 2005 Apr;39(4):449-55 |
|
5 |
Edmond Kato Kabagambe, Jeremy Furtado, Ana Baylin, and Hannia Campos - Some Dietary and Adipose Tissue Carotenoids Are Associated with the Risk of Nonfatal Acute Myocardial Infarction in Costa Rica1,2 - J. Nutr. 135: 1763–1769, 2005. [File =142 JN 2005.pdf] |
|
6 |
Kohlmeier L, Kark JD, Gomez-Gracia E, Martin BC, Steck SE, Kardinaal AF, Ringstad J, Thamm M, Masaev V, Riemersma R, Martin-Moreno JM, Huttunen JK, Kok FJ - Lycopene and myocardial infarction risk in the EURAMIC Study. Am J Epidemiol 1997 Oct 15;146(8):618-626 [File : 6AmJEpid1997.pdf] |
|
7 |
Gerster H - Vitamin Research Department, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Basel, Switzerland. The potential role of lycopene for human health. J Am Coll Nutr 1997 Apr;16(2):109-126 |
|
8 |
Klipstein-Grobusch K, Launer LJ, Geleijnse JM, Boeing H, Hofman A, Witteman JC - Department of Epidemiology & Biostatistics, Erasmus University Medical School, Rotterdam, The Netherlands. Serum carotenoids and atherosclerosis. The Rotterdam Study. Atherosclerosis 2000 Jan;148(1):49-56 |
|
9 |
Arab L, Steck S - School of Public Health, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill. Lycopene and cardiovascular disease. Am J Clin Nutr 2000 Jun;71(6 Suppl):1691S-5S; discussion 1696S-7SV [File : 9AmJClinNutr2000.pdf] |
|
10 |
Rao AV, Agarwal S – Department of Nutritional Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Role of antioxidant lycopene in cancer and heart disease J Am Coll Nutr 2000 Oct;19(5):563-9 Review [ File : 10JAmCollNutr2000.pdf] |
|
11 |
Hsueh YM, Wu WL, Huang YL, Chiou HY, Tseng CH, Chen CJ - Department of Public Health, School of Medicine, Taipei Medical College, Taiwan, ROC. Low serum carotene level and increased risk of ischemic heart disease related to long-term arsenic exposure. Atherosclerosis 1998 Dec;141(2):249-57 |
|
12 |
Agarwal S, Rao AV - Department of Nutritional Sciences, University of Toronto, ON, Canada Carotenoids and chronic diseases. Drug Metabol Drug Interact 2000;17(1-4):189-210 |
|
13 |
Fuhrman B, Elis A, Aviram M - Lipid Research Laboratory, Technion Faculty of Medicine, Rappaport Family Institute for Research in the Medical Sciences, Haifa, Israel. Hypocholesterolemic effect of lycopene and betacarotene is related to suppression of cholesterol synthesis and augmentation of LDL receptor activity in macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1997 Apr 28;233(3):658-662 . [File : 15BBRC1997.pdf] |
|
14 |
Agarwal S, Rao AV - Department of Nutritional Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, University of Toronto, Ont. Tomato lycopene and its role in human health and chronic diseases. CMAJ 2000 Sep 19;163(6):739-44 [File : 16CMAJ2000.pdf] |
|
15 |
Frei B - Boston University School of Medicine, Whitaker Cardiovascular Institute, Massachusetts 02118, USA. Cardiovascular disease and nutrient antioxidants: role of low-density lipoprotein oxidation. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 1995 Jan;35(1-2):83-98 |
|
16 |
Street DA, Comstock GW, Salkeld RM, Schuep W, Klag MJ - Department of Epidemiology, Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Health, Baltimore, Md. Serum antioxidants and myocardial infarction. Are low levels of carotenoids and alpha-tocopherol risk factors for myocardial infarction? Circulation 1994 Sep;90(3):1154-1161 [Full text ; file: 19 Circulation 1994.pdf] |
|
17 |
Rissanen T, Voutilainen S, Nyyssonen K, Salonen R, Salonen JT - Research Institute of Public Health, University of Kuopio, Finland, and Inner Savo Health Centre (J.T.S.), Finland. Low plasma lycopene concentration is associated with increased intima-media thickness of the carotid artery wall. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2000 Dec;20(12):2677-81 [File : 21ArtThrVascBiol2000.pdf] |
|
18 |
Paul Knekt; John Ritz; Mark A. Pereira; Eilis J O’Reilly; Katarina Augustsson; Gary E. Fraser; Uri Goldbourt; Berit L. Heitmann; Goran hallmans ; Simin Liu ; Pirjo Pietinen ; Donna Spiegelmam ; June Stevens ; Jarmo Vitarmo; Walter C. Willet; Eric B. Rimm; Alberto Ascherio; Antioxidant Vitamins and Coronary Heart Disease risk : a pooled analysis of 9 Cohorts. Am J. Clin Nutr. 2004; 80 : 1508-20 [File : 22AJCN2004.pdf] |
|
19 |
Dugas TR; Morel DW; Harrison EH - Impact of LDL carotenoid and alpha-tocopherol content on LDL oxidation by endothelial cells in culture - Journal of Lipid Research 1998, Vol 39, Iss 5, pp 999-1007 [File : 23 JlipRes1998.pdf] |
|
20 |
Aviram M, Fuhrman B - Lipid Research Laboratory, Technion Faculty of Medicine, Rappaport Family Institute for Research in the Medical Sciences, Haifa, Israel. LDL oxidation by arterial wall macrophages depends on the oxidative status in the lipoprotein and in the cells: role of prooxidants vs. antioxidants. Mol Cell Biochem 1998 Nov;188(1-2):149-59 |
|
21 |
Tertov VV, Sobenin IA, Kaplun VV, Orekhov AN - Institute of Experimental Cardiology, Cardiology Research Center, Moscow, Russia - Antioxidant content in low density lipoprotein and lipoprotein oxidation in vivo and in vitro. Free Radic Res 1998 Aug;29(2):165-73 |
|
22 |
Plat J, van Onselen EN, van Heugten MM, Mensink RP - Department of Human Biology, Maastricht University, Maastricht, The Netherlands. Effects on serum lipids, lipoproteins and fat soluble antioxidant concentrations of consumption frequency of margarines and shortenings enriched with plant stanol esters. Eur J Clin Nutr 2000 Sep;54(9):671-7 |
|
23 |
Hoffmann J, Linseisen J, Riedl J, Wolfram G - Institute of Nutritional Sciences, Technical University of Munich. Dietary fiber reduces the antioxidative effect of a carotenoid and alpha-tocopherol mixture on LDL oxidation ex vivo in humans. Eur J Nutr 1999 Dec;38(6):278-85 |
|
24 |
Cockey CD - Lycopene may contribute to heart health. AWHONN Lifelines 2002 Jun-Jul;6(3):206 |
|
25 |
Carroll YL, Corridan BM, Morrissey PA - Department of Food Science and Technology, University College Cork, Ireland. Lipoprotein carotenoid profiles and the susceptibility of low density lipoprotein to oxidative modification in healthy elderly volunteers. Eur J Clin Nutr 2000 Jun;54(6):500-7 |
|
26 |
Giugliano D - Dipartimento di Gerontologia, Geriatria e Malattie del Metabolismo, Seconda Universita di Napoli, Italy. Dietary antioxidants for cardiovascular prevention. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2000 Feb;10(1):38-44 |
|
27 |
Martin KR, Wu D, Meydani M - Vascular Biology Program, Jean Mayer USDA Human Nutrition Research Center on Aging at Tufts University, 711 Washington Street, 02111, Boston, MA, USA. The effect of carotenoids on the expression of cell surface adhesion molecules and binding of monocytes to human aortic endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2000 Jun;150(2):265-74 |
|
28 |
Upritchard JE, Sutherland WH, Mann JI - Department of Human Nutrition, University of Otago, Dunedin, New Zealand. Effect of supplementation with tomato juice, vitamin E, and vitamin C on LDL oxidation and products of inflammatory activity in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000 Jun;23(6):733-8 |
|
29 |
Linseisen J, Hoffmann J, Riedl J, Wolfram G - Institute of Nutrition Science of the Technical University of Munich, Freising-Weihenstephan, Freising-Weihenstephan, D-85350, Germany - Effect of a Single Oral Dose of Antioxidant Mixture (Vitamin E, Carotenoids) on the Formation of Cholesterol Oxidation Products after ex vivo LDL Oxidation in Humans. Eur J Med Res 1998 Feb 21;3(1/2):5-12 |
|
30 |
Fuhrman B, Volkova N, Rosenblat M, Aviram M - Lipid Research Laboratory, Technion Faculty of Medicine, The Rappaport Family Institute for Research in the Medical Sciences and Rambam Medical Center, Haifa, Israel. Lycopene synergistically inhibits LDL oxidation in combination with vitamin E, glabridin, rosmarinic acid, carnosic acid, or garlic. Antioxid Redox Signal 2000 Fall;2(3):491-506 |
|
31 |
Clinton, S. K.; Craft, N. E.; Degroff, V. L.; Hadley, C.W.; Harris, G. K.; Miller, B. C.; Schwartz, S. J The consumption of processed tomato products enhances plasma lycopene concentrations and reduces oxidative damage to lipoproteins in humans. FASEB Journal VOL. 15 NO. 4 March 7, 2001 PP. A297. March 31- April 04, 2001 Annual Meeting of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology on Experimental Biology 2001 |
|
32 |
Rissanen TH, Voutilainen S, Nyyssonen K, Lakka TA, Sivenius J, Salonen R, Kaplan GA, Salonen JT. Research Institute of Public Health, University of Kuopio, PO Box 1627, FIN-70211, Kuopio, Finland. Low serum lycopene concentration is associated with an excess incidence of acute coronary events and stroke: the Kuopio Ischaemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study. Br J Nutr 2001 Jun;85(6):749-54 |
|
33 |
Paran, Esther; Engelhard, Yehiel - Hypertension Unit, Soroka University medical Center, Beer Sheva, Israel Effect of tomato's lycopene on blood pressure, serum lipoproteins, plasma homocysteine and oxidative stress markers in grade I hypertensive patients. American Journal of Hypertension Vol. 14 N. 4 Part 2- April, 2001 PP. 141A. May 15-19, 2001 [Abstract : 49AJH2001.pdf] |
|
34 |
Tonomoto, Mariko; Maruyama, Chizuko; Imamura, Kayoko; Harada, Miho; Egami, Satoko; Baba, Naoko; Ayaori, Makoto; Inakuma, Takahiro; Ishikawa, Toshitsugu; Oshima, Shunji; Suzukawa, Michio - Department of Food and Nutrition, Japan Women's University, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo, 112-8681, Japan - Effects of tomato juice consumption on plasma and lipoprotein carotenoid concentrations and the susceptibility of low density lipoprotein to oxidative modification. Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology VOL.47 N.3 June, 2001 PP. 213-221 |
|
35 |
Dexter L. Morris, Stephen B. Kritchevsky ; C.E. Davis. Serum Carotenoids and Coronary Heart Disease. Jama 1994 ; Vol.272 , N.18 ; 1439-1441. [File : 55Jama1994.pdf] |
|
36 |
McQuillan BM, Hung J, Beilby JP, Nidorf M, Thompson PL. Gairdner Campus of the Heart Research Institute of Western Australia, Western, Nedlands, Perth, Australia Antioxidant vitamins and the risk of carotid atherosclerosis. The perth carotid ultrasound disease assessment study (CUDAS). J Am Coll Cardiol 2001 Dec;38(7):1788-1794 - [File : 57 JACC 2001.pdf] |
|
37 |
Gianetti J, Pedrinelli R, Petrucci R, Lazzerini G, De Caterina M, Bellomo G, De Caterina R. C. N. R. Institute of Clinical Physiology, University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy. Inverse association between carotid intima-media thickness and the antioxidant lycopene in atherosclerosis. Am Heart J 2002 Mar;143(3):467-74 [File : 58AmHeartJ2002.pdf] |
|
38 |
Ruiz Rejon F, Martin-Pena G, Granado F, Ruiz-Galiana J, Blanco I, Olmedilla B. - Servicio de Cardiologia, Servicio de Medicina Interna, Hospital de Mostoles, Madrid, Spain. Plasma status of retinol, alpha- and gammatocopherols, and main carotenoids to first myocardial infarction: case control and follow-up study. Nutrition 2002 Jan;18(1):26-31 |
|
39 |
Tero Hirvoven; Jarmo Virtamo ; Pasi Korhonen ; Demetrius Albanes ; Pirjo Pietinen. Intake of Flavonoids , carotenoids ,Vitamin C, Vitamin E and Risk of Stroke in Male Smokers. Journal of the American Heart Association. Stroke 2000; 31 ; 2301-2306 . [File : 68Stroke2000.pdf] |
|
40 |
A.Elisabeth Hak; Jing Ma; Calpurnya B.Powell; Hannia Campos; J.Michael Gaziano; Walter C.Willet;Meier Stampfer. Prospective Study of Plasma Carotenoids and Tocopherols in relation to risk of Ischemic Stroke. Journal of the American Heart Association. Stroke 2004; 35 ; 1584-1588 . [File : 69Stroke2004.pdf] |
|
41 |
Tavani A, Gallus S, Negri E, Parpinel M, La Vecchia C. - Istituto di Ricerche Farmacologiche "Mario Negri", Via Eritrea 62, Milan, 20157, Italy. Dietary intake of carotenoids and retinol and the risk of acute myocardial infarction in Italy. Free Radic Res. 2006 Jun;40(6):659-64. |
|
42 |
Bansal P, Gupta SK, Ojha SK, Nandave M, Mittal R, Kumari S, Arya DS. - Department of Pharmacology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Ansari Nagar, New Delhi, 110029, India. Cardioprotective effect of lycopene in the experimental model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Cell Biochem. 2006 Apr 7 |
|
43 |
Engelhard YN, Gazer B, Paran E. - Hypertension Unit, Faculty of Health Sciences, Soroka University Medical Centre, Ben Gurion, University of the Negev, 84101 Beer Sheva, Israel. Natural antioxidants from tomato extract reduce blood pressure in patients with grade-1 hypertension: double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Am Heart J. 2006 Jan;151(1):100. [File : 72AmHeartJ2006.pdf] |
|
44 |
Kaliora AC, Dedoussis GV, Schmidt H. - Department of Science of Dietetics-Nutrition, Harokopio University of Athens, Greece. Dietary antioxidants in preventing atherogenesis. Atherosclerosis. 2005 Nov 25 |
|
45 |
Karimi G, Ramezani M, Abdi A. Department of Pharmacodynamy and Toxicology, School of Pharmacy, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran. Protective effects of lycopene and tomato extract against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Phytother Res. 2005 Oct;19(10):912-4. Copyright (c) 2005 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. |
|
46 |
Hsiao G, Wang Y, Tzu NH, Fong TH, Shen MY, Lin KH, Chou DS, Sheu JR. - Graduate Institute of Pharmacology, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan. Inhibitory effects of lycopene on in vitro platelet activation and in vivo prevention of thrombus formation. J Lab Clin Med. 2005 Oct;146(4):216-26 |
|
47 |
Yilmaz S, Atessahin A, Sahna E, Karahan I, Ozer S. - Department of Biochemistry, College of Veterinary Medicine, Faculty of Veterinary, Firat (Euphrates) University, Turkey. Protective effect of lycopene on adriamycin-induced cardiotoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Toxicology. 2006 Feb 1;218(2-3):164-71. Epub 2005 Dec 1 |
|
48 |
Sesso HD, Buring JE, Norkus EP, Gaziano JM. - Divisions of Preventive Medicine and Aging, Department of Medicine, Brigham & Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA. Plasma lycopene, other carotenoids, and retinol and the risk of cardiovascular disease in men. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005 May;81(5):990-7. [Full text ; file : 77AmJClinNutr2005.pdf] |
|
49 |
Sesso HD. - Divisions of Preventive Medicine and Aging, Department of Medicine, Brigham & Women's Hospital and Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts Veterans Epidemiology Research and Information Center, VA Boston Healthcare System, Boston, Massachusetts, USA. Carotenoids and cardiovascular disease: what research gaps remain? Curr Opin Lipidol. 2006 Feb;17(1):11-16. |
|
50 |
Sesso HD, Buring JE, Norkus EP, Gaziano JM. - Division of Preventive Medicine, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's , Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02215, USA. Plasma lycopene, other carotenoids, and retinol and the risk of cardiovascular disease in women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004 Jan; 79(1): 47- 53. [File : 79 AJCN 2004.pdf |
|
51 |
Rissanen TH, Voutilainen S, Nyyssonen K, Salonen R, Kaplan GA, Salonen JT. Research Institute of Public Health (THR, SV, KN, RS, and JTS) and the Department of Public Health and General Practice (THR and JTS), University of Kuopio, Kuopio, Finland. Serum lycopene concentrations and carotid atherosclerosis: the Kuopio Ischaemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study. Am J Clin Nutr 2003 Jan;77(1):133-8 [File : 80AmJClinNutr2003.pdf] |
|
52 |
Willcox JK, Catignani GL, Lazarus S. - Dept. of Food Science, North Carolina State University, Raleigh 27695- 7624, USA. Tomatoes and cardiovascular health. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2003;43(1):1-18 |
|
53 |
Osganian SK, Stampfer MJ, Rimm E, Spiegelman D, Manson JE, Willett WC. Dietary carotenoids and risk of coronary artery disease in women. Am J Clin Nutr. 2003 Jun;77(6):1390-9. [File : 82AmJClinNutr2003.pdf] |
|
54 |
Hak AE, Stampfer MJ, Campos H, Sesso HD, Gaziano JM, Willett W, Ma J. - Department of Epidemiology, Harvard School of Public Health, Channing Laboratory, 181 Longwood Ave, Boston, Mass 02115-5804, USA. Plasma carotenoids and tocopherols and risk of myocardial infarction in a low-risk population of US male physicians. Circulation. 2003 Aug 19;108(7):802-7. Epub 2003 Aug 04. [File : 83Circulation2003.pdf |
|
55 |
Ahuja KD, Pittaway JK, Ball MJ. - School of Human Life Sciences, University of Tasmania, Launceston, Tasmania, Australia. Effects of olive oil and tomato lycopene combination on serum lycopene, lipid profile, and lipid oxidation. Nutrition. 2006 Jan 12; |
|
56 |
Chang CY, Chen JY, Ke D, Hu ML. Department of Neurology, Chi-Mei Foundation Hospital, Tainan, Taiwan, ROC. Plasma levels of lipophilic antioxidant vitamins in acute ischemic stroke patients: correlation to inflammation markers and neurological deficits. Nutrition. 2005 Oct;21(10):987-93 |
|
57 |
M.A.Newaz; N.N.A. Nawal– Faculty of Medicine Kuala Lampur - Malysia – Effect of alfa–tocopherol on lipid peroxidation and total antioxidant status in spontaneously hyeprtensive rats. The American Journal of Hypertension . AJH 1998 ; 11:1480-1485. [File : 91AJH1998.pdf] |
|
58 |
Ohkawa S, Yoneyama T, Shimoi K, Takita T, Maruyama Y, Kumagai H. Department of Clinical Nutrition, School of Food and Nutritional Sciences and COE Program in the 21st Century, University of Shizuoka, 52-1 Yada, Shizuoka Japan. Pro-oxidative effect of alpha-tocopherol in the oxidation of LDL isolated from coantioxidant- depleted non-diabetic hemodialysis patients. Atherosclerosis. 2004 Oct;176(2):411-8 |
|
59 |
Lee DH, Gross MD, Jacobs Jr DR. Department of Preventive Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, South Korea. Association of Serum Carotenoids and Tocopherols with {gamma}- Glutamyltransferase: The Cardiovascular Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) Study. Clin Chem. 2004 Jan 15 |
|
60 |
Hadley CW, Clinton SK, Schwartz SJ. - The Department of Food Science and Technology, The James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute, Columbus, OH 43210, USA. -The consumption of processed tomato products enhances plasma lycopene concentrations in association with a reduced lipoprotein sensitivity to oxidative damage. J Nutr 2003 Mar;133(3):727-32 [File : 97 JNutr2003.pdf] |
|
61 |
Visioli F, Riso P, Grande S, Galli C, Porrini M. Department of Pharmacological Science, University of Milan,Italy. Protective activity of tomato products on in vivo markers of lipid oxidation. Eur J Nutr. 2003 Aug;42(4):201-6 |
|
62 |
Jonasson L, Wikby A, Olsson AG. - Department of Cardiology, Heart Center, University Hospital, S-581 85 Linkoping, Sweden. Low serum beta-carotene reflects immune activation in patients with coronary artery disease. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2003 Jun;13(3):120-5 |
|
63 |
Passi S, Stancato A, Aleo E, Dmitrieva A, Littarru GP. Centro Invecchiamento Cellulare, I.D.I. (IRCCS), Roma, Italy. Statins lower plasma and lymphocyte ubiquinol/ubiquinone without affecting other antioxidants and PUFA. Biofactors. 2003; 18(1-4): 113-24. |
|
64 |
Kerstin Kilpstein-Grobusch ; Johanna H. den Breeeijen; Dieterick E. Grobbe ; Alimer Boeing ; Albert Hofman; Jacqueline C.D. Witherman. Dietary Antioxidant and Peripheral Arterial Disease. The Rotterdam Study. The American Journal of Epidemiology. AJE 2001. Vol. 154 N0.2. [file : 107AJE2001.pdf |
|
65 |
Kaumudi J Joshipura; Frank B. Hu; JoAnn E. Manson; Meier J. Stampfer ; Eric B. Rimm ; Frank E. Spelzen; Graham Colditz; Alberto Ascherio; Bernard Rosner ; Donna Spiegelmam ; Walter C. Willet. The effect of Fruits and Vegetable intake on Risk for Coronary Heart Disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2001; 134: 1106-1114. [File : 108AIM2001.pdf |
|
66 |
Lenore Kohlmeier and Susan B. Hastings - Epidemiologic evidence of a role of carotenoids in cardiovascular disease prevention. Am J Clin Nutr 1995 : 62 (suppl) : 1370S-6S [file : 109 AmJClinNutr1995.pdf |
|
67 |
Louis J. Ignarro , Maria Luisa Balestrieri, Claudio Napoli. Nutrition, physical activity and cardiovascular disease: an update. Review Cardiovascular Research 73 (2007) 326-340 [file : 110CardioRes2007.pdf |
|
68 |
Atshshi Hozawa, D.R. Jacobs, et ... Relationship of circulating carotenoid concentrations with several markers of inflammation, oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction : the Coronary Artery Risk Development In Young Adult (CARDIA) / Young Adult Longitudinal Trend in Antioxidants (YALTA) study -Cardiovascular Research 73 (2007) 326-340 [file : 111ClinChem2007.pdf] |
|
69 |
H.D. Sesso, Simin Liu, J.Michael Graziano and J.E. Buring. Dietary Lycopene, Tomato based product and cardiovascular disease in women. The Journal of Nutrition. J. Nutr 133 : 2336-2341 , 2003 [file : 112JNutr2003.pdf] |
|
70 |
Marlene M. Most Estimated phytochemical content of the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) Diet is higher than in the control study diet. J. Am Diet Ass. 2004- 104 :1725-1727 [file : 113JAmDietAss 2004.pdf |
|
71 |
Paran Esther; Engelhard Yehiel, Inbal Hazan-Hallevy, Yoav Sharoni, Joseph Levy - Hypertension Unit, Soroka University medical Center, Beer Sheva, Israel - Effect of standardized tomato extract on blood pressure, endothelial function and plasma Lycopene level in treated hypertensive patients. American Journal of Hypertension Vol. 18 No. 5 Part 2- May 2005 [Abstract : 114AJH2005.pdf |
|
72 |
Sudesh Vasdev ; Vicki Gill - Department of medicine and laboratory medicine, Health Sciences Centre, Memorial University of Newfoundland St.John’s , Newfoundland , Canada - Antioxidants in the treatment of Hypertension. International Journal of Angiology 14 :60-73 (2005) [ File : 115IJA2005.pdf |
|
73 |
K. Asplund - Department of Medicine- University Hospital – Stockholm , Sweden. Pierre srl – Galatina, Italy–Dietary Supplement with Organic Lycopene (Patent n.WO/2008/015490). LICOMPLETE™ was developed by Pierre, working with University of Salento and CNR (National Research Centre) Antioxidant Vitamins in the prevention of cardiovascular disease. Review - Journal of Internal Medicine 251: 372-392 (2002) [File : 116JIM2002.pdf |
|
74 |
J.H.Johnn ; S.Ziebland ; P Yudkin ; L.S.Roe; H.A.Neil – Oxford Fruit and Vegetable Study Group. Effect of fruit and vegetable on plasma antioxidant concentrations and blood pressure : a randomised controlled trial – Lancet 2002; 359 : 1969-74 [File : 117Lancet2002.pdf] |
|
75 |
Brendan M. Mc.Quillan; Joseph Hung ; John P. Beilby ; Mark Nidorf ; Peter L. Thompson. CLINICAL STUDIES. Antioxidant vitamins and the risk of carotenoid atherosclerosis : the perth carotid ultrasound disease assessment study (CUDAS) – J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001 ; 38; 1788-1794 [File : 119 JACC2001.pdf] |
|
76 |
Alberto Ascherio ; Eric B. Rimm; Miguel A. Hernan; Edward Giovannucci ; Ichiro Kawachi; Meir J. Stompfer; Walter C. Willet. Relation of Consumption of Vitamin E, Vitamin C and Carotenoid to risk fort Stroke among the men in United States Am. Int. Med. 1999 ; 130; 963-970 [File:120AmIntMed 1999.pdf |
|
77 |
Stephen B. Kritchevsky. Department of Preventive Medicine , University of Tennesee. Memphis. B. Carotene, Carotenoids and the prevention of Coronary Heart Disease – J. Nutr. 1999; Vol 129 ; 5-8 [File : 121JNutr1999.pdf] |
|
78 |
Francene M. Steinberg and Alan Chait. Antioxidant vitamin supplementation and lipid peroxidation in smokers – Am J. Clin Nutr. 1998; Vol 68 ; 319-27 [File : 122AmJClinNutr1998.pdf |
|
79 |
Stephen B. Krichevinsky ; Andrew J. Bush ; Marco Pahor ; Myran D. Gross. Serum Carotenoids and Markers of Inflammation in Nonsmokers. American Journal of Epidemiology. AJE 2000 ; Vol. 152 N.11 ; 1065 –71 [File : 125AJE2000.pdf |
|
80 |
A.V. Rao and S.Agarwal. Department of Sciences ,University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Effect of diet and smoking on serum Lycopene and Lipid peroxidation. Nutritional Research , Vol 18, No 4 , p 713-721, 1998 [File : 126NR1998.pdf |
|
81 |
Tammy M. Bray, PhD - Dean and Professor College of Health and Human Sciences Oregon State University Corvallis- OR - Putative Anti-inflammatory Functions of Lycopene in Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease [File : 127 Bray Presentation.pdf] |
|
82 |
Milde J, Elstner EF, Grassmann J. Department of Plant Sciences, Institute of Phytopathology, Laboratory for Applied Biochemistry, Munich Technical University, Freising-Weihenstephan, Germany. Synergistic effects of phenolics and carotenoids on human low-density lipoprotein oxidation. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2007 Aug;51(8):956-61. |
|
83 |
Steinberg D., Parthasarathy S., Care T.E., Khoo J.C., Witztum J.L. Beyond cholesterol: Modifications of lowdensity lipoprotein that increases its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med 1989: 320:915-924 |
|
84 |
Parthasarathy S. Mechanisms by which dietary antioxidants may prevent cardiovascular diseases. J Medicinal Food 1998; 1:45-51 |
|
85 |
Street D.A., Comstock G.W., Salkeld R.M., Schuep W., Klag M.J. Serum antioxidants and myocardial infarction. Are levels of carotenoids and alpha-tocopherol risk factors for myocardial infarction? Circulation 1994; 90:1154-1161 |
|
86 |
Kristenson M., Zieden B., Kucinaskiene Z., Elinder L.S., Bergdahl B., Elwing B., Abaravicius A., Razinkoviene L., Calkauskas H., Olsson A. Antioxidant State and Mortality from Coronary Heart Disease in Lithuanian and Swedish Men: Concomitant Cross Sectional Study of Men Aged 50. BMJ 1997; 314:629-633 |
|
87 |
G. Riccioni, B. Mancini, E. Di Ilio, T. Bucciarelli, N.D’Orazio - Protective effect of lycopene in cardiovascular disease - European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2008; 12: 183-190 [File 135 ERMPS 2008.pdf] |
|
88 |
Linseisen J., Hoffmann J., Riedl J., Wolfram G. Effect of a single dose of antioxidant mixture (vitamin E, carotenoids) on the formation of cholesterol oxidation products after ex vivo LDL oxidation in humans. Eur J Med Res 1998; 3:5-12. Pierre srl – Galatina, Italy–Dietary Supplement with Organic Lycopene (Patent n.WO/2008/015490). LICOMPLETE™ was developed by Pierre, working with University of Salento and CNR (National Research Centre) |
|
89 |
Agarwal S., Rao A.V. Tomato lycopene and low-density lipoprotein oxidation: a human dietary intervention study. Lipids 1998; 33:981-984 |
|
90 |
Lu Wang, J. Michael Gaziano, Edward P. Norkus, Julie E Buring, and Howard D. Sesso- Associations of plasma carotenoids with risk factors and biomarkers related to cardiovascular disease in middle-aged and older women - Am J Clin Nutr. 2008 September ; 88(3): 747–754. [File 138 AJCN 2008.pdf] |
|
91 |
Peter W. de Leeuw & Aalt Bast - Tomato Extract for Hypertension? Editorial to “The Effects of Natural Antioxidants from Tomato Extract in Treated but Uncontrolled Hypertensive Patients” by E. Paran et al. - Cardiovasc Drugs Ther (2009) 23:107–108 [File 139 CDT 2009.pdf] |
|
92 |
Hussein O, Frydman G, Frim H, Aviram M. Lipid Research Laboratory, Government Rebecca Sieff Hospital, P.O. Box 1008, 13100, Safed, Israel - Reduced susceptibility of low density lipoprotein to lipid peroxidation after cholestyramine treatment in heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemic children. Pathophysiology 2001 Aug;8(1):21-28 |
|
93 |
Frank B Hu, Eric B Rimm, Meir J Stampfer, Alberto Ascherio, Donna Spiegelman, and Walter C Willett - Prospective study of major dietary patterns and risk of coronary heart disease in men1–3 -. Am J Clin Nutr 2000;72:912–21. [File 141 AJCN 2000.pdf |
|
|
Heart supplements |
|
CARDIOVASCULAR RISK - PROTECTING YOUR HEALTH |
|
LYCOMPLETE - LYCOPENE EXTRACTED FROM ORGANIC TOMATOES BY SUPERCRITICAL CO2 FREE OF CHEMICAL SOLVENTS |
|
|
|
|
LYCOPENE SOURCES Lycopene is a carotenoid, a group of compounds present in many fresh fruits and vegetables. There are more than 750 types of carotenoids in nature; however, only 20 of these have been found in human blood and tissues. The carotenoid most often present in human blood is lycopene ,followed by b -carotene, lutein and zeaxanthin. |
|
|
RED RIPE TOMATOES
THE MAIN SOURCE OF LYCOPENE and their derivatives are the main natural source of
lycopene giving approximately 85% of all lycopene in the human body. The
amount of lycopene in tomatoes depends the quality of fruit, the
environment and cultivation procedures. Usually, the content of lycopene
in red-ripe tomatoes is 30-80 mg/kg of fresh product, but it could be
more than 150-300 mg/kg in some selected species obtained by traditional
hybridization techniques. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Health Prostate Dietary |
Lycodeep skin care supplement |
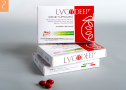
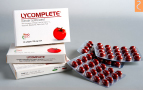
Lycomplete heart supplement |
Lycosport athlete supplements |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
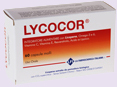
Lycocor for Italian market |
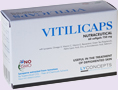
Vitilicaps for Santo Domingo market |
Naturmio women for Italian market |
Lycofor (eyes optic) for Italian market |
 |
 |
We offer our full dietary, food and health care supplements manufacturing knowledge plus our engineering capabilities to create, design, produce new supplement products, in Private label, for manufacturers and distributors. |
|
Naturmio Health Prostate for Italy |
Lycocor for Spain and Portugal market |
| DUBAI MANUFACTURING VENDORS |
|
DUBAI INDUSTRIAL MANUFACTURING |
 |
Dubai Business Guide in Europe your Gateway to the Arab manufacturing suppliers and vendors direct from Dubai. Equipments, gears machines, Real estate, technology suppliers, leather furniture manufacturing, machinery supplies, power transmission suppliers, Beauty care, wine vendors, oil, shoes, automotive furniture from Dubai to USA and Europe |
|
|
Dubai Business Guide list of Dubai manufacturing, suppliers, vendors and professional companies from Dubai qualified to support directly your business at manufacturing pricing and customer service, Dubai beauty care, chemical industry, clothing, fashion apparel, machinery, industrial supplies, electronics, furniture, automotive spare parts, engineering... |
|
FOR INFORMATION ABOUT DUBAI AND MIDDLE EAST BUSINESS CALL: +39-333.6371.644 |
|
The Dubai Business Guide engineers work hard to support the Dubai, USA, Italian manufacturing and industrial suppliers in Dubai, Italy, China, USA and worldwide distribution companies creating business to business relationship. Through the Dubai women apparel and lingerie manufacturing, Arab electronics Dubai suppliers, Abu Dhabi machinery suppliers, Middle East power transmission gears manufacturer, industrial Dubai petrochemical supplies, Dubai Arab real estate vacations, Dubai business equipment Arab suppliers, health care medicines web pages to your business goal. Made in Dubai, women apparel, electronics, lingerie, jewelry, Dubai electrical motors manufacturing, petrol chemical vendors and business suppliers of Dubai Business Guide offered on our site. Products made in Dubai to Italy, the USA (New York, Atlanta, Texas, Miami, California, New jersey), England, Ireland, Norway, Russia, Canada, Japan, Korea, Kuwait, Oman, Japan, Australia, China, Germany, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Russia, Denmark, Norway, Taiwan, Australia, England, Germany, Austria, Mexico, Brasil, Canada, Brasil, New Zeland, Italy, Austria, France, Holland, Spain, Scotland, Sweden, Netherlands, Venezuela, Colombia, Peru, Chile, Argentina... and worldwide business to business wholesale distribution market |
|
|
|
About us Listing your Business in Dubai Business Guide Worldwide Business to Business Middle East Arab Vendors |
|
We invite you to visit our following Dubai Business to Business web pages - Site map |
|
DUBAI BUSINESS GUIDE "YOUR GATEWAY TO THE MIDDLE EAST MANUFACTURING SUPPLIERS" |
|||
|
Italy in EUROPE |
Miami Florida in the U.S.A. |
Beijing in CHINA |
|
|
For info and customer services Email: info@dubaimanufacturing.com |
|||
|
2000 - 2019 Dubai
Business Guide, Inc. & Da-BI.N Group Inc. Network |